
|
|

| Troubleshooting | News | Technical | Search |
| Home | Forum 56 | Premium | Site Map |
 |
|
||||||||
 |
|
||||||||
| Home • Troubleshooting • Modem Log | |||||||||
Windows 95/98/NT/2k/Me/XP all include the ability to record a modem log. This log can help you pinpoint a variety of problems you might encounter while attempting to make a connection.
The information below applies to Windows 95/98. See this page for Windows 2000 & XP Modemlog.
| Windows 95: The Option to record a
log file is set from: Start -> Settings -> Control Panel-> Modems -> Click your Modem listing, Click Properties Click the Connection tab Click Advanced On Advanced Connection Settings, set the checkbox Record a Log file. Click OK all the way out. Note: This is also the area you enter any Extra settings, or initialization string for your modem. Windows 98, 2K, ME & XP have similar options. - see Windows 2000/XP log setup. |
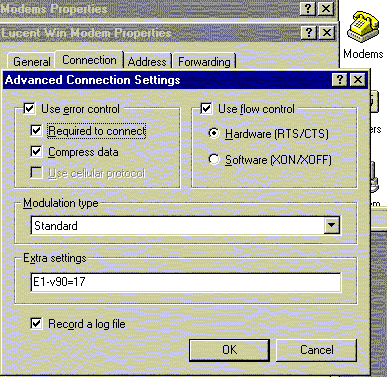 |
| Finding your Modemlog: Your next challenge is to locate the log. In Windows 95 & NT, the log is named Modemlog.txt. In Windows 98 and higher, it will be named <modemname>.log, where modemname is the name displayed in the modem list (above). Later versions of Windows will have a 'View Log' button on the modem properties screen to open the log. Use Find Files to locate your log file. (Win98 name shown w/ wildcard) |
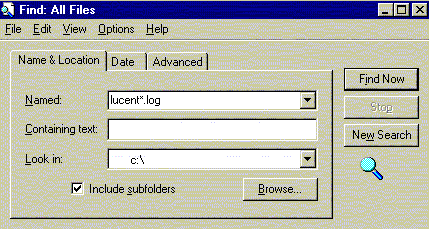 |
| Once you've found your modem log file, open it with Notepad. (Notepad is good because it defaults to Courier fixed-space font.) | The pane below shows parts of a modem log file. All entries have the date & time which is shown only on the first line to save space. |
|
The modem log will identify the modem, the
name of the .inf file beings used, as well as the section of the .inf file.
When the modem disconnects, it is logged - and may contain information about the disconnect. |
Modem Log Output 05-23-2000 08:30:33.292 - Lucent Win Modem
in use. |
Port settings - With a software-controller modem like the Lucent used in this example, a 'virtual' COM port is used - these port settings don't matter and the modem isn't limited to the port speed rate. Hardware modems that use a 'real' COM port are limited by this setting, and in most cases, 115.2k is the desired setting.Extra settings or init string - Note that your string follows the basic initialization of the modem, and in many cases is unnecessary. I do not recommend using a string if you don't know what it does, and if you do use a string, you should avoid &F, Z, W1 and other 'modem altering drugs'.
The modem is told to Dial... And in a somewhat unusual and inefficient way, I might add. Notice how the modem is first given the ATD; command, and waits for the OK response before sending another D command with the actual number.
Disconnection - When the modem disconnects, log entries are made (the format and type of entries will vary among different versions of Windows). Some of the responses that may be seen include:
Hanging Up the Modem
Hardware hangup by lowering DTRYou (or something running on your computer) caused the disconnect NO CARRIER The modem couldn't establish, or lost a connection and hung up Remote modem hung up The modem at your ISP disconnected you TSP(0000): Dropping Call
Hanging up the modem.
Hardware hangup by lowering DTR.
Detected CD dropped from lowering DTR
WindowsXP log entries when you (or something running on your computer) caused the disconnect. Also see:
Modem Diagnostic Screens
Disconnections
| Home | Links | Send
Feedback | Privacy Policy | Report Broken Link Legal Page | Author's Web Sites | Log In |
|
Modemsite.com ©1998-2022 v.Richard Gamberg. All rights reserved. |